Permutation Tests
Contents
Permutation Tests#
from datascience import *
from cs104 import *
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
1. Load and explore maternal smoker data#
First stage of our data science pipeline, let’s explore the data and see if we find something interesting.
You can read more about this data here.
births = Table.read_table('data/baby.csv')
births.show(4)
| Birth Weight | Gestational Days | Maternal Age | Maternal Height | Maternal Pregnancy Weight | Maternal Smoker |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 | 284 | 27 | 62 | 100 | False |
| 113 | 282 | 33 | 64 | 135 | False |
| 128 | 279 | 28 | 64 | 115 | True |
| 108 | 282 | 23 | 67 | 125 | True |
... (1170 rows omitted)
smoking_and_birthweight = births.select('Maternal Smoker', 'Birth Weight')
smoking_and_birthweight.group('Maternal Smoker')
| Maternal Smoker | count |
|---|---|
| False | 715 |
| True | 459 |
smoking_and_birthweight.hist('Birth Weight', group='Maternal Smoker')
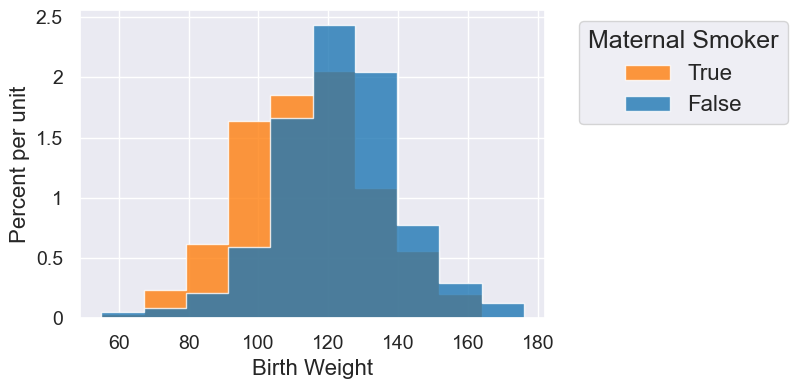
Interesting! It looks like there’s a higher birth weight for maternal non-smokers. But is this just due to chance? Let’s use hypothesis testing to find out.
2. Test Statistic#
means_table = smoking_and_birthweight.group('Maternal Smoker', np.mean)
means_table
| Maternal Smoker | Birth Weight mean |
|---|---|
| False | 123.085 |
| True | 113.819 |
means = means_table.column('Birth Weight mean')
observed_difference = means.item(0) - means.item(1)
observed_difference
9.266142572024918
In keeping with the approach we laid out last lecture, we’ll focus only on absolute difference…
observed_difference = abs(means.item(0) - means.item(1))
observed_difference
9.266142572024918
def abs_difference_of_means(table, group_label, value_label):
# table containing group means
means_table = table.group(group_label, np.mean)
# array of group means
means = means_table.column(value_label + ' mean')
return abs(means.item(0) - means.item(1))
Our observed difference
observed_difference = abs_difference_of_means(births, 'Maternal Smoker', "Birth Weight")
observed_difference
9.266142572024918
We can use this function on lots of columns!
abs_difference_of_means(births, 'Maternal Smoker', "Maternal Age")
0.8076725017901509
abs_difference_of_means(births, 'Maternal Smoker', "Maternal Height")
0.09058914941267915
3. Simulation Under Null Hypothesis#
Creating Permutations of Labels#
Just use a tiny table to show our approach…
tiny_smoking_and_birthweight = smoking_and_birthweight.take(np.arange(0,6))
tiny_smoking_and_birthweight
| Maternal Smoker | Birth Weight |
|---|---|
| False | 120 |
| False | 113 |
| True | 128 |
| True | 108 |
| False | 136 |
| False | 138 |
We’ll use .sample(with_replacement=False) to shuffle the rows of a table.
shuffled_labels = tiny_smoking_and_birthweight.sample(with_replacement=False).column('Maternal Smoker')
shuffled_labels
array([ True, False, False, False, True, False])
original_and_shuffled = tiny_smoking_and_birthweight.with_columns('Shuffled Label',
shuffled_labels)
original_and_shuffled
| Maternal Smoker | Birth Weight | Shuffled Label |
|---|---|---|
| False | 120 | True |
| False | 113 | False |
| True | 128 | False |
| True | 108 | False |
| False | 136 | True |
| False | 138 | False |
A function to make a permutation!
def permutation_sample(table, group_label):
"""
Returns: The table with a new "Shuffled Label" column containing
the shuffled values of the group_label.
"""
# array of shuffled labels
shuffled_labels = table.sample(with_replacement=False).column(group_label)
# table of numerical variable and shuffled labels
shuffled_table = table.with_columns('Shuffled Label', shuffled_labels)
return shuffled_table
original_and_shuffled = permutation_sample(tiny_smoking_and_birthweight,
"Maternal Smoker")
original_and_shuffled
| Maternal Smoker | Birth Weight | Shuffled Label |
|---|---|---|
| False | 120 | True |
| False | 113 | False |
| True | 128 | True |
| True | 108 | False |
| False | 136 | False |
| False | 138 | False |
We’ll calculate the statistic for the shuffled groups.
abs_difference_of_means(original_and_shuffled, "Shuffled Label", "Birth Weight")
0.25
And now the full table…
smoking_and_birthweight
| Maternal Smoker | Birth Weight |
|---|---|
| False | 120 |
| False | 113 |
| True | 128 |
| True | 108 |
| False | 136 |
| False | 138 |
| False | 132 |
| False | 120 |
| True | 143 |
| False | 140 |
... (1164 rows omitted)
original_and_shuffled = permutation_sample(smoking_and_birthweight,
"Maternal Smoker")
original_and_shuffled
| Maternal Smoker | Birth Weight | Shuffled Label |
|---|---|---|
| False | 120 | False |
| False | 113 | False |
| True | 128 | True |
| True | 108 | False |
| False | 136 | False |
| False | 138 | False |
| False | 132 | False |
| False | 120 | False |
| True | 143 | True |
| False | 140 | True |
... (1164 rows omitted)
Statistic for one sample of the null hypothesis.
abs_difference_of_means(original_and_shuffled, 'Shuffled Label', 'Birth Weight')
2.9358593476240458
Permutation Test#
Our simulate_permutation_statistic function is in the library. Here’s the full code. It’s just a minor variation on our usual simulation code!
def simulate_permutation_statistic(table, group_label, value_label, num_trials):
sample_statistics = make_array()
for i in np.arange(num_trials):
one_sample = permutation_sample(table, group_label)
sample_statistic = abs_difference_of_means(one_sample,
"Shuffled Label",
value_label)
sample_statistics = np.append(sample_statistics, sample_statistic)
return sample_statistics
simulated_birth_weight_diffs = simulate_permutation_statistic(smoking_and_birthweight,
'Maternal Smoker',
'Birth Weight',
1000)
results = Table().with_columns('abs(Group A Mean - Group B Mean)',
simulated_birth_weight_diffs)
plot = results.hist()
plot.set_title("Null hypothesis empirical distribution")
plot.dot(observed_difference)
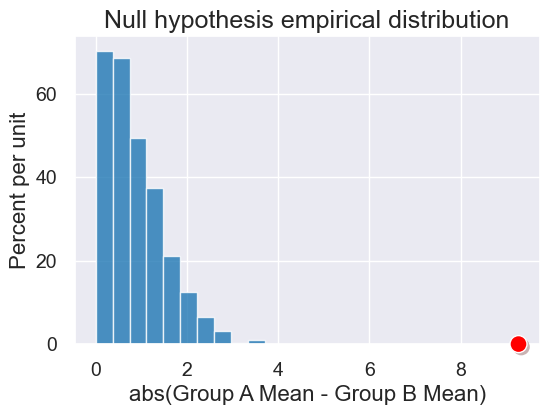
Let’s calculate the p-value (even if we can easily guess what it is here)…
np.count_nonzero(simulated_birth_weight_diffs >= observed_difference) / len(simulated_birth_weight_diffs)
0.0
Or, even better… Use our function!
empirical_pvalue(simulated_birth_weight_diffs, observed_difference)
0.0
3. A second hypothesis test#
Is the Maternal Age of smokers different than non-smokers?
observed_difference = abs_difference_of_means(births, 'Maternal Smoker', "Maternal Age")
simulated_birth_weight_diffs = simulate_permutation_statistic(births,
'Maternal Smoker',
'Maternal Age',
1000)
results = Table().with_columns('abs(Group A Mean Age - Group B Mean Age)',
simulated_birth_weight_diffs)
plot = results.hist(left_end=observed_difference)
plot.set_title("Null hypothesis empirical distribution")
plot.dot(observed_difference)
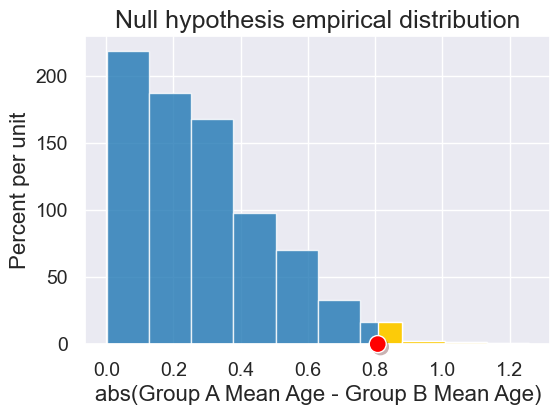
empirical_pvalue(simulated_birth_weight_diffs, observed_difference)
0.02

