Inference Library Reference
Inference Library Reference#
Click on any row to see detailed examples.
Library Sections
- Sampling and Simulation
- Hypothesis Testing
- Permutation Tests
- Bootstrapping and Confidence Intervals
- Linear Regression
Sampling and Simulation
| Name | Description | Parameters | Output | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
array : each item corresponds to the proportion of times that corresponding item was sampled from model_proportions in sample_size draws, should sum to 1 |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Simulates the outcome of |
|
An array of the simulated outcomes. |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Simulates the process of computing a statistic for random samples. |
|
An array of the simulated statistics. |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
Hypothesis Testing
| Name | Description | Parameters | Output | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Computes the proportion of values in |
|
A proportion. |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
Permutation Tests
| Name | Description | Parameters | Output | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Returns the given table augmented with a new column |
|
A new Table. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Takes a table, the label of the column used to divide rows into two groups, and the label of the column storing the values for each row. Returns: the absolute difference of means for the two groups. Note: If the values are all 0 or 1, then the result can be interpreted as the difference in the proportion of 1 for the two groups. |
|
A float. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Simulates |
|
An array of the simulated statistics. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bootstrapping and Confidence Intervals
| Name | Description | Parameters | Output | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Simulates the process of computing a statistic for resamples of one original sample. The original sample
is represented as a array, and the |
|
An array of the simulated statistics for the resamples. |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Returns an array with the lower and upper bound of the |
|
An array of two elements. |
|||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
Linear Regression
| Name | Description | Parameters | Output | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Computes the correlation coefficient capturing the sign and strength of the association between the given columns in the table. |
|
A float between -1 and 1. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Computes the prediction y_hat = a * x + b where a and b are the slope and intercept and x is the set of x-values. |
|
an array of predicted y values. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Computes the slope and intercept of the line best fitting the table’s data according to the mean square error loss function. |
|
A two-element array with the slope and intercept. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Given the values \(x\) and \(y\) in the |
|
A float between 0 and 1. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Plots a scatter graph for the points in given columns and also a line for the equation \(y = ax+b\). |
|
A Plot. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Given the values \(x\) and \(y\) in the |
|
A Plot. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
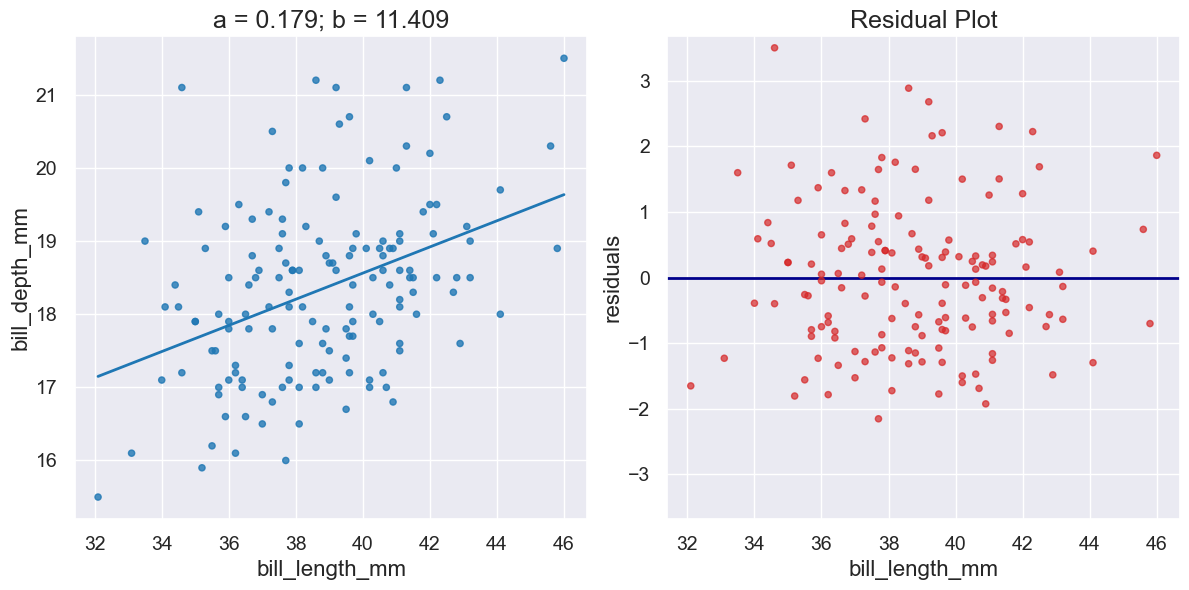
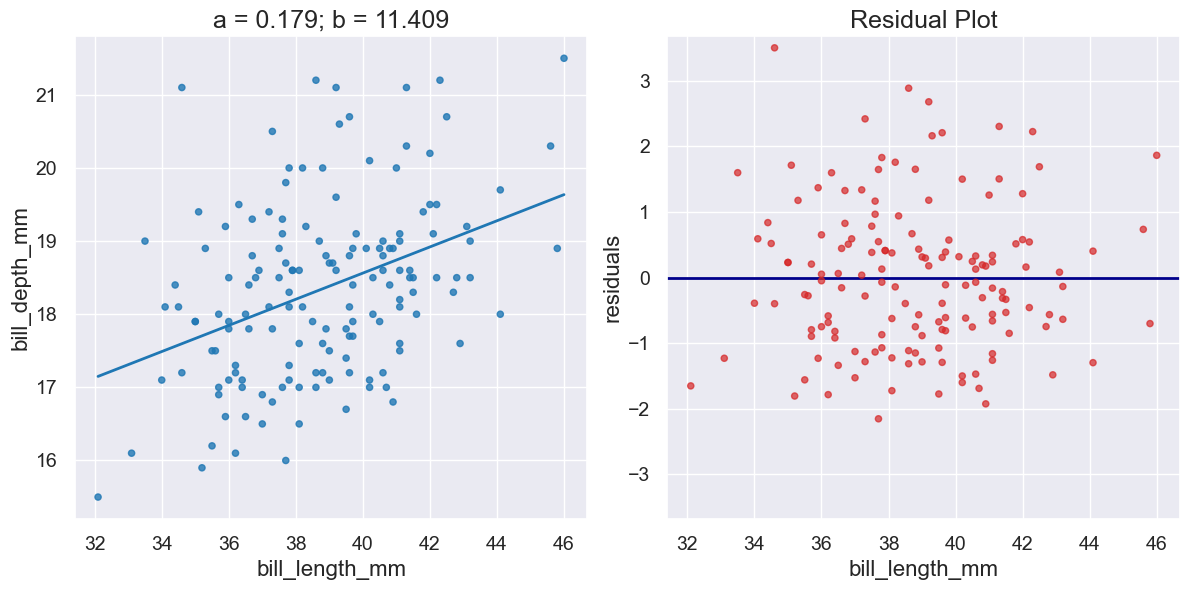
Create a pair of plots capturing 1) a scatter plot and the line \(y=ax+b\) and 2) the residuals when that line is used for preductions. Returns the Plot for the scatter plot. |
|
A Plot. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||