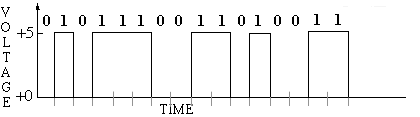
s(t) = 2 x V x (d(t) - 1/2)
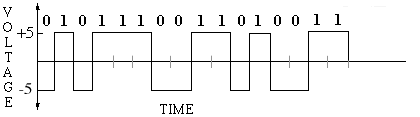
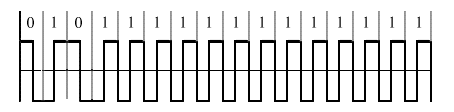
This scheme is knows as Non-Return to Zero (NRZ) signalling.
This causes two problems:
- The signal will again have a direct current component (although I must admit that I have too little background to really explain why this is bad).
- The receiver and sender will have to have precisely synchronized and highly accurate clocks since the signal itself will provide no information to enable the receiver to detect any drift in its clock.
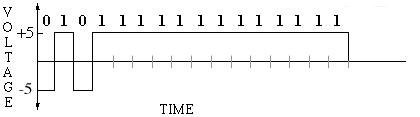
 = 0 = 0 |
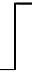 = 1 = 1
|
- At the sending end of the fiber, an electrical signal
produced by the computer is used to control a light
emitting diode or laser producing a beam of light whose
intensity varies to reflect the bits being transmitted.
- At the receiving end, a photo detector converts the light back into an electrical signal.