GraphDrawingPack: Implementation Design and Details
Introduction
GraphDrawingPack contains all the methods for drawing a graph. The
GraphCanvas has a variable of type GraphDrawingInterface, which is
currently instantiated to GraphDrawing. Each Edge has its own
object of type EdgeDrawingInterface to implement drawing that edge,
and similarly each Vertex contains an object of type
VertexDrawingInterface which implements drawing that vertex.
GraphDrawingPack is made up of:
- GraphDrawingInterface
- implemented by: GraphDrawing.java
- VertexDrawingInterface
- implemented by: VertexDrawing.java
- EdgeDrawingInterface
- implemented by: EdgeDrawing.java, DirEdgeDrawing.java, DirEdgeStraight.java
- EdgeShapeInterface
- implemented by: Arrow.java, Implementing.java, Inherits.java,
Aggregation.java
Edges and Vertices
Drawing a directed edge is difficult since if there are two
edges between a pair of vertices then the edge must bow outward.
Since it would be inefficient to recalculate the arc for a bowed out
edge each time the edge is drawn, the information needed to draw the
edge is stored. We wanted to separate the graph data structure from
the details of drawing the graph as much as possible, so all the
classes to draw graphs, vertices, and edges are in GraphDrawingPack.
DirEdge contains a variable of type EdgeDrawingInterface (from
GraphDrawingPack) and currently instatiates it to DirEdgeDrawing.
Whenever one of DirEdge's vertices is moved, or another edge is added
between its two vertices, the information to draw the edge must be
recomputed, thus an update() function is called.
To be consistent, we did the same for vertices. Each vertex
contains a variable of type VertexDrawingInterface, and instantiates
it, currently to VertexDrawing. No information needs to be
updated however, so drawing vertices is easier than edges.
Object Model
Here is the object model for the GraphDrawingPack. As usual, classes
are represented as boxes, circle edges represent "implements", arrow
edges represent "contains" or "has a pointer to", and large triangles
represent "inherits from".
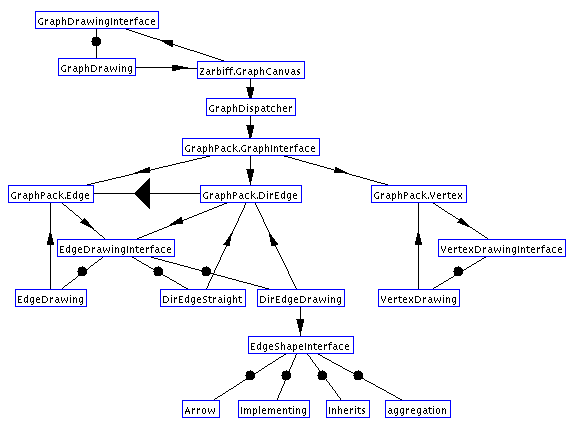
Changes
To change how edges (vertices) are drawn, you would need to:
- Write a class which implements EdgeDrawingInterface.
- Change the instantiation the EdgeDrawingInterface in Edge.java
and/or DirEdge.java from "drawing = new EdgeDrawing(this)" to
"drawing = new ()"
Edge Shapes
EdgeShape refer to the shape drawn at the midpoint of a directed
edge. The default EdgeShape is ARROW, but three other choices are
available:
- INHERITS: a large triagle
- IMPLEMENTING: a circle
- AGGREGATION: a diamond
The EdgeShape can be changed by a user from the edge menu.
To add an edge shape, implement EdgeShapeInterface and add the name to
DirEdgeDrawing.setShape. Also write a filter which calls
DirEdgeDrawing.setShape and add this filter to the .zarbiff file so
that it appears on the menu.
"Straight" Directed Edges
Currently, if there are two directed edges between a pair of vertices,
they are drawn as bowed out arcs. However, due to a rounding error in
java.awt's drawArc() method, the arcs often do not reach to the
vertices - which looks terrible. Thus we implemented an alternative
to bowed edges by placing both arrows on the same straight line
(called straight edges for lack of a better name). The two arrows are
a fixed distance from each other, which causes some problems when the
vertices are either close together or very large. Straight edges can
only have arrows, not any of the other edge shapes, for no real reason other than lack of time.
The way to switch from bowed to straight edges is currently a hack -
and should be reprogrammed. The GraphCanvas holds a variable edgetype
which stores whether edges are to be drawn straight or bowed. When
edges are drawn, the EdgeDrawingInterface class checks to see whether
to draw the edges bowed or straight. Thus every edge creates a
drawing() variable of type DirEdgeDrawing, but when the edge gets
drawn a new DirEdgeStraight is created if GraphCanvas.edgetype =
"straight".

