Midterm Review Session
Midterm Review Session#
This is the code we wrote during the review session.
# Run this cell to set up the notebook.
# These lines import the numpy, datascience, and cs104 libraries.
import numpy as np
from datascience import *
from cs104 import *
%matplotlib inline
Here’s a loop that inspects the contents of an array and does something to each element:
for word in make_array("Cow", "Goat", "Dog"):
print(word)
Cow
Goat
Dog
Here’s a loop that does “something” a specific number of times (also known as a counting loop):
dice = np.arange(1,7)
for i in np.arange(0,5):
print(np.random.choice(dice))
4
6
5
1
5
Here’s a loop that inspects elements of an array and counts the number elements that meet some criteria. In this case, we are counting the positive numbers:
def stay_positive(values):
count = 0
for i in values:
if i > 0:
count = count + 1
return count
This is a version of the same function that uses array broadcasting and np.count_nonzero:
stay_positive(make_array(1,-1,-2,3,4,0))
def stay_positive(values):
return np.count_nonzero(values > 0)
stay_positive(make_array(1,-1,-2,3,4,0))
3
Here is a simple simulation loop that rolls 100 dice and counts the number of times we see a 6. We look at one outcome at a time and tally the outcomes matching our criteria:
dice = np.arange(1,7)
count = 0
for i in np.arange(0, 100):
if np.random.choice(dice) == 6:
count = count + 1
count
21
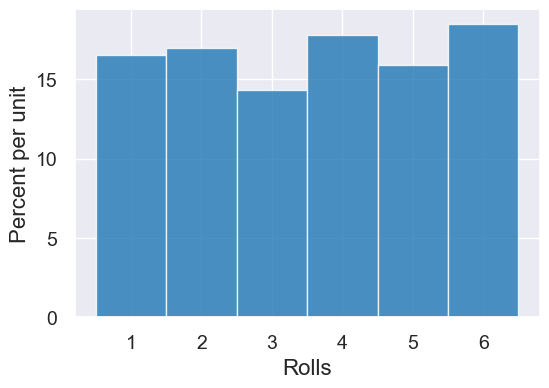
Here is a simple simulation loop that collects the outcomes of 1000 dice rolls in an array. That way, we can look at all outcomes after the simulation and, for example, plot a histogram:
dice = np.arange(1,7)
result = make_array()
for i in np.arange(0, 1000):
roll = np.random.choice(dice)
result = np.append(result, roll)
Table().with_columns("Rolls", result).hist(bins=np.arange(0.5,7.5,1))
Here are some apply examples:
finches = Table().read_table('data/finch_beaks_1975.csv')
finches.show(3)
| species | Beak length, mm | Beak depth, mm |
|---|---|---|
| fortis | 9.4 | 8 |
| fortis | 9.2 | 8.3 |
| scandens | 13.9 | 8.4 |
... (403 rows omitted)
Let’s add a new column that is the Beak length in inches.
def to_inch(mm):
return mm / 25.4
to_inch(10)
0.3937007874015748
inches = finches.apply(to_inch, 'Beak length, mm')
new_finches = finches.with_columns('Beak Length, in', inches)
new_finches
| species | Beak length, mm | Beak depth, mm | Beak Length, in |
|---|---|---|---|
| fortis | 9.4 | 8 | 0.370079 |
| fortis | 9.2 | 8.3 | 0.362205 |
| scandens | 13.9 | 8.4 | 0.547244 |
| scandens | 14 | 8.8 | 0.551181 |
| scandens | 12.9 | 8.4 | 0.507874 |
| fortis | 9.5 | 7.5 | 0.374016 |
| fortis | 9.5 | 8 | 0.374016 |
| fortis | 11.5 | 9.9 | 0.452756 |
| fortis | 11.1 | 8.6 | 0.437008 |
| fortis | 9.9 | 8.4 | 0.389764 |
... (396 rows omitted)
Let’s compute a “beak area” too. (Okay, this is stretching credulity a bit, but it lets us demonstrate using apply with a function of two arguments.
def area(depth, length):
return depth * length
areas = finches.apply(area, 'Beak depth, mm', 'Beak length, mm')
areas
array([ 75.2 , 76.36 , 116.76 , 123.2 , 108.36 , 71.25 ,
76. , 113.85 , 95.46 , 83.16 , 112.7 , 99.36 ,
101.7 , 109.25 , 102.35 , 85.36 , 105.73 , 107.365 ,
89.89 , 90.1 , 78.72 , 95.79 , 95.55 , 92.4 ,
102.46 , 107.52 , 79.9 , 81.81 , 76.8 , 101.85 ,
81.18 , 83.16 , 75.84 , 99.51 , 123.9 , 98.94 ,
104.64 , 71.61 , 113.68 , 109.76 , 85.85 , 98.44 ,
111.1 , 97.2 , 91.8 , 101.52 , 91.52 , 110.88 ,
112.86 , 97.01 , 97.76 , 79.54 , 83.64 , 74.52 ,
84.84 , 111.1 , 88.58 , 86.7 , 106.7 , 113.3 ,
86.86 , 99.51 , 95.23 , 106.7 , 122.4 , 118.32 ,
84.15 , 95.04 , 93.45 , 87. , 89.28 , 106.7 ,
97.92 , 76.145 , 106.56 , 96.72 , 108.78 , 89.76 ,
93.73 , 89.1 , 114.4 , 97.2 , 99.75 , 91.35 ,
107.52 , 105.28 , 111.15 , 90.3 , 103.95 , 105.28 ,
91. , 89.44 , 100.44 , 102.12 , 90.64 , 102.12 ,
81.34 , 92.4 , 103.4 , 116.48 , 83.3 , 77.42 ,
77.42 , 104.03 , 110.74 , 83. , 104.34 , 90. ,
86.52 , 88.74 , 95.68 , 104.5 , 116.15 , 115.64 ,
86.7 , 119.34 , 86.86 , 94.86 , 85.26 , 94.34 ,
84. , 124.63 , 109.89 , 93.45 , 91. , 87.72 ,
75.66 , 86. , 101.65 , 104.5 , 111.18 , 95.55 ,
105.73 , 100.58 , 124.95 , 91.8 , 102.9 , 112. ,
102.72 , 98.88 , 114.84 , 97.65 , 104.64 , 74.48 ,
100.28 , 90.64 , 118.17 , 97.9 , 93.1 , 85.28 ,
104.76 , 107.8 , 98.58 , 110.74 , 88.88 , 115.14 ,
123.9 , 85.14 , 106.7 , 108. , 109.61 , 116.55 ,
114.4 , 95.68 , 73.71 , 101.52 , 94.34 , 71.34 ,
99.51 , 88.58 , 94.5 , 69.16 , 82.65 , 105.84 ,
99.64 , 98.01 , 116.15 , 109.76 , 76.63 , 131.76 ,
72.68 , 105. , 88.2 , 102.6 , 94.16 , 122.72 ,
73.71 , 98.98 , 82. , 104.5 , 128.1 , 110.58 ,
104.64 , 101.76 , 73.47 , 110.09 , 98.58 , 113.3 ,
71.1 , 100.1 , 92.56 , 86.32 , 90.24 , 100.7 ,
85.85 , 83.42 , 81.6 , 82.82 , 78.21 , 110. ,
102.46 , 77.6 , 86. , 93.6 , 114.84 , 76.8 ,
103.68 , 100.28 , 91.8 , 91.8 , 95.68 , 104.5 ,
98.44 , 107.67 , 98.28 , 102.46 , 85.14 , 115.64 ,
77.6 , 123.76 , 77.76 , 107.91 , 87.72 , 79.2 ,
101.7 , 105.73 , 79.38 , 90.64 , 66. , 118.32 ,
81.18 , 85.14 , 86.13 , 89.44 , 110.88 , 102.6 ,
83.16 , 86.13 , 83.64 , 95.68 , 77.08 , 93.84 ,
102.3 , 94.34 , 94.5 , 94.64 , 89.76 , 89.76 ,
105.6 , 113.22 , 79.54 , 93.45 , 98.1 , 94.16 ,
108.9 , 101.37 , 110.88 , 109.25 , 108. , 90.78 ,
107.8 , 107.91 , 91.35 , 99.36 , 80.36 , 76.63 ,
93.73 , 85.49 , 85.49 , 125.28 , 125.28 , 107.91 ,
95.4 , 106.95 , 103.68 , 100.719 , 119.646 , 87.978 ,
129.8934, 117.5004, 103.008 , 95.8624, 97.185 , 108.382 ,
100.9245, 114.954 , 98.4555, 84.405 , 117.915 , 83.555 ,
80.0253, 104.94 , 123.0768, 113.3884, 95.497 , 88.131 ,
92.8725, 112.2975, 96.9075, 84.2175, 91.7375, 126.3125,
110.0475, 111.1425, 89.1475, 85.4025, 117.3625, 99.9375,
89.9475, 116.76 , 123.2 , 108.36 , 108. , 101.91 ,
129.94 , 111.8 , 120.7 , 124.6 , 129.22 , 112.66 ,
147.98 , 110.7 , 129.6 , 144.53 , 110.94 , 106.6 ,
134.1 , 117.6 , 118.68 , 115.7 , 134.225 , 113.71 ,
120.06 , 134.4 , 124.1 , 138.32 , 121.5 , 138.92 ,
148.5 , 110.08 , 137.08 , 128.52 , 119.26 , 120.7 ,
157.04 , 144.96 , 127.4 , 126.48 , 130.2 , 123.2 ,
115.37 , 123.2 , 135.59 , 157.56 , 122.82 , 132.48 ,
108.8 , 144.84 , 135.34 , 128.8 , 143.56 , 129.22 ,
114.75 , 109.88 , 131.4 , 125.55 , 109.6 , 126.49 ,
106.11 , 111.22 , 120.06 , 119.68 , 120.4 , 117.45 ,
102.4 , 123.2 , 120.6 , 135.59 , 151.3596, 133.133 ,
144.354 , 163.592 , 123.089 , 150.4736, 136.8656, 128.07 ,
128.0575, 138.4775, 141.2775, 120.6675, 132.7725, 137.4975,
127.1525, 126.4375, 142.2225, 110.6375])
finches_with_area = finches.with_columns('Beak area, mm^2', areas)
finches_with_area.show(3)
| species | Beak length, mm | Beak depth, mm | Beak area, mm^2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| fortis | 9.4 | 8 | 75.2 |
| fortis | 9.2 | 8.3 | 76.36 |
| scandens | 13.9 | 8.4 | 116.76 |
... (403 rows omitted)
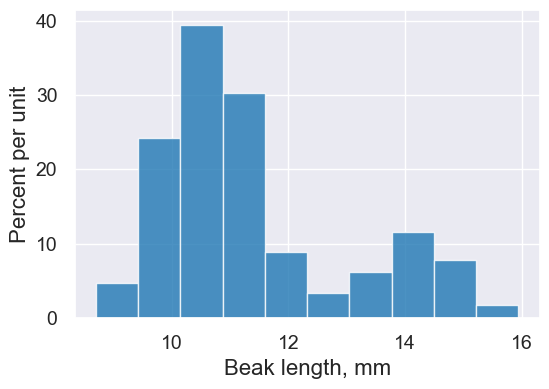
Overlaid histograms enable us to divide rows of a table into groups that are displayed separately. Compare this histogram:
finches.hist('Beak length, mm')
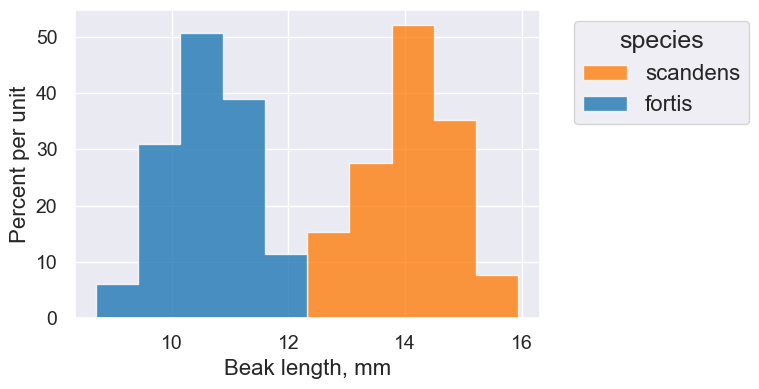
to this one, where we group our observations by species. It lets us identify the characteristics of our different groups much more easily.
finches.hist('Beak length, mm', group='species')
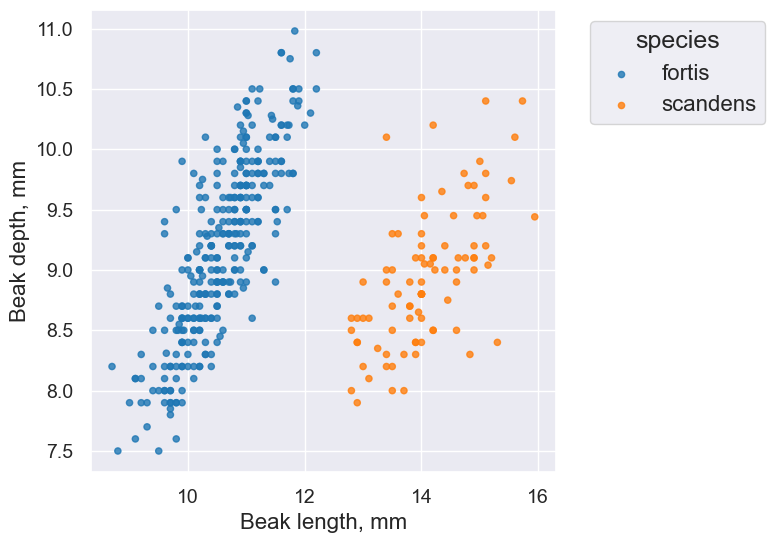
One last example:
finches.scatter('Beak length, mm', 'Beak depth, mm', group='species')