
public interface Graph extends Collection
{
public void add(Object label);
// pre: label is a non-null label for vertex
// post: a vertex with label is added to graph.
// if vertex with label is already in graph, no action.
public void addEdge(Object vtx1, Object vtx2, Object label);
// pre: vtx1 and vtx2 are labels of existing vertices
// post: an edge (possibly directed) is inserted between
// vtx1 and vtx2.
public Object remove(Object label);
// pre: label is non-null vertex label
// post: vertex with "equals" label is removed, if found
public Object removeEdge(Object vLabel1, Object vLabel2);
// pre: vLabel1 & vLabel2 are labels of existing vertices
// post: edge is removed, its label is returned
public Object get(Object label);
// post: returns actual label of indicated vertex
public Edge getEdge(Object label1, Object label2);
// post: returns actual label of edge between vertices.
public boolean contains(Object label);
// post: return true iff vertex w/ "equals" label exists.
public boolean containsEdge(Object vLabel1,Object vLabel2);
// post: returns true iff edge with "equals" label exists
public boolean visit(Object label);
// post: sets visited flag on vertex, returns prev. value
public boolean visitEdge(Edge e);
// pre: sets visited flag on edge; returns previous value
public boolean isVisited(Object label);
// post: returns visited flag on labelled vertex
public boolean isVisitedEdge(Edge e);
// post: returns visited flag on edge between vertices
public void reset();
// post: resets visited flags to false
public int size();
// post: returns the number of vertices in graph
public int degree(Object label);
// pre: label labels an existing vertex
// post: returns the no. of vertices adjacent to vertex
public int edgeCount();
// post: returns the number of edges in graph
public Iterator elements();
// post: returns iterator across all vertices of graph
public Iterator neighbors(Object label);
// pre: label is label of vertex in graph
// post: returns iterator over vertices adj. to vertex
// each edge beginning at label visited exactly once
public Iterator edges();
// post: returns iterator across edges of graph
// iterator returns edges; each edge visited once
public void clear();
// post: removes all vertices from graph
public boolean isEmpty();
// post: returns true if graph contains no vertices
public boolean isDirected();
// post: returns true if edges of graph are directed
}
class Vertex
{
protected Object label; // the user's label
protected boolean visited; // this vertex visited
public Vertex(Object label)
// post: constructs unvisited vertex with label
{
Assert.pre(label != null, "Vertex key is non-null");
this.label = label;
visited = false;
}
public Object label()
// post: returns user label associated w/vertex
{
return label;
}
public boolean visit()
// post: marks vertex as being visited.
{
boolean was = visited;
visited = true;
return was;
}
public boolean isVisited()
// post: returns true iff vertex has been visited
{
return visited;
}
public void reset()
// post: marks vertex unvisited
{
visited = false;
}
public boolean equals(Object o)
// post: returns true iff vertex labels are equal
{
Vertex v = (Vertex)o;
return label.equals(v.label());
}
}
========================================================
public class Edge
{
protected Object[] vLabel; // labels of adjacent vertices
protected Object label; // edge label
protected boolean visited; // this edge visited
protected boolean directed; // this edge directed
public Edge(Object vtx1, Object vtx2, Object label, boolean directed)
// post: edge associates vtx1 & vtx2. labeled with label.
// directed if "directed" set true
{
vLabel = new Object[2];
vLabel[0] = vtx1;
vLabel[1] = vtx2;
this.label = label;
visited = false;
this.directed = directed;
}
public Object here()
// post: returns first node in edge
{
return vLabel[0];
}
public Object there()
// post: returns second node in edge
{
return vLabel[1];
}
public void setLabel(Object label)
// post: sets label of this edge to label
{
this.label = label;
}
public Object label()
// post: returns label associated with this edge
{
return label;
}
public boolean visit()
// post: visits node, returns whether previously visited
{
boolean was = visited;
visited = true;
return was;
}
public boolean isVisited()
// post: returns true iff node has been visited
{
return visited;
}
public void reset()
// post: resets edge's visited flag to initial state
{
visited = false;
}
public boolean equals(Object o)
// post: returns true iff edges connect same vertices
{
Edge e = (Edge)o;
return ((here().equals(e.here()) &&
there().equals(e.there())) ||
(!directed && (here().equals(e.there()) &&
there().equals(e.here()))));
}
}
If there are a fixed number of edges from each node then
we can have fixed number of edges stored with each node (like a binary
tree).
Otherwise we typically use an adjacency matrix or adjacency lists.
Example: Here is an undirected graph of the Northeastern states.
NY, VT, NH, ME, MA, CN, RI
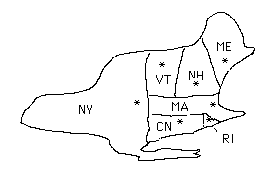
We will draw a line between capitals if the corresponding states share a common border:
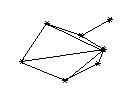
We will represent this graph as both an adjacency matrix and an adjacency list.
Labels of vertices are stored in a dictionary, so we can look up corresponding index for each vertex label.
| NY | VT | NH | ME | MA | CN | RI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NY | null | 2 | null | null | 1 | 1 | null |
| VT | 2 | null | 1 | null | 1 | null | null |
| NH | null | 1 | null | 1 | 3 | null | null |
| ME | null | null | 1 | null | null | null | null |
| MA | 1 | 1 | 3 | null | null | 1 | 1 |
| CN | 1 | null | null | null | 1 | null | 1 |
| RI | null | null | null | null | 1 | 1 | null |
If the graph is undirected, then we can just keep the lower (or upper) triangular part, since the matrix is symmetric.
First define abstract GraphMatrix, then two subclasses, GraphMatrixDirected and GraphMatrixUndirected, which add in missing method bodies for adding, removing, and iterating through edges.
It is simple to add and delete edges.
Addition of or finding node is also simple. (Though there is a clear problem in adding a new node if all rows or columns in the array are already filled.)
Deleting node may require shifting all following nodes over to fill hole (unless we just leave the hole!).
Solve by keeping a list of available indices for vertices and pull off one when it's needed.
Clearly with n nodes, this representation requires an array with n2 slots.
In order to implement a GraphMatrix, we will first extend our notion of a vertex so that the vertex can remember its index in the matrix. class GraphMatrixVertex extends Vertex { protected int index; public GraphMatrixVertex(Object label, int idx) // post: constructs a new augmented vertex { super(label); index = idx; } public int index() // post: returns index associated with vertex { return index; } public String toString() // post: returns string representation of vertex { return "<GraphMatrixVertex: "+label()+">"; } } And now we can implement the GraphMatrix class.
abstract public class GraphMatrix implements Graph
{
protected int size; // allocation size for graph
protected Edge data[][]; // matrix - array of arrays
protected Dictionary dict; // translate labels ->
// vertices
protected List freeList; // available indices in matrix
protected boolean directed; // graph is directed
protected GraphMatrix(int size, boolean dir)
// pre: size > 0
// post: construct an empty graph that may be expanded to
// at most size vertices. Graph directed if dir true
// and undirected otherwise
{
this.size = size; // set maximum size
directed = dir; // fix direction of edges
// the following constructs a size x size matrix
data = new Edge[size][size];
// label to index translation table
dict = new Hashtable(size); // come back to later
// put all indices in the the free list
freeList = new SinglyLinkedList();
for (int row = size-1; row >= 0; row--)
freeList.add(new Integer(row));
}
public void add(Object label)
// pre: label is a non-null label for vertex
// post: a vertex with label is added to graph.
// if vertex with label is already in graph, no action.
{
// if there already, do nothing.
if (dict.containsKey(label)) return;
Assert.pre(!freeList.isEmpty(), "Matrix not full");
// allocate a free row and column
int row = ((Integer) freeList.removeFromHead()).intValue();
// add vertex to dictionary
dict.put(label, new GraphMatrixVertex(label, row));
}
abstract public void addEdge(Object v1, Object v2, Object label);
// pre: v1 & v2 are labels of existing vertices
// post: an edge (possibly directed) inserted btn v1 & v2
// if edge new, it is labeled with label (can be null)
public Object remove(Object label)
// pre: label is non-null vertex label
// post: vertex with "equals" label is removed, if found
{
// find and extract vertex
GraphMatrixVertex vert;
vert = (GraphMatrixVertex)dict.remove(label);
if (vert == null) return null;
// remove vertex from matrix
int index = vert.index();
// clear row and column entries
for (int row=0; row<size; row++) {
data[row][index] = null;
data[index][row] = null;
}
// add node index to free list
freeList.add(new Integer(index));
return vert.label();
}
abstract public Object removeEdge(Object vLabel1, Object vLabel2);
// pre: vLabel1 & vLabel2 are labels of existing vertices
// post: edge is removed, its label is returned
public Object get(Object label)
// post: returns actual label of vertex with label "equals" 'label'
{
GraphMatrixVertex vert;
vert = (GraphMatrixVertex) dict.get(label);
return vert.label();
}
public Edge getEdge(Object label1, Object label2)
// post: returns actual edge between vertices.
{
int row,col;
row = ((GraphMatrixVertex) dict.get(label1)).index();
col = ((GraphMatrixVertex) dict.get(label2)).index();
return data[row][col];
}
public boolean contains(Object label)
// post: return true iff vertex w/ "equals" label exists.
{
return dict.containsKey(label);
}
public boolean containsEdge(Object vLabel1, Object vLabel2)
// post: returns true iff edge with "equals" label exists
{
GraphMatrixVertex vtx1, vtx2;
vtx1 = (GraphMatrixVertex) dict.get(vLabel1);
vtx2 = (GraphMatrixVertex) dict.get(vLabel2);
Assert.condition(vtx1 != null, "Vertex exists");
Assert.condition(vtx2 != null, "Vertex exists");
return data[vtx1.index()][vtx2.index()] != null;
}
public boolean visit(Object label)
// post: sets visited flag on vertex,
// returns previous value
{
Vertex vert = (Vertex) dict.get(label);
return vert.visit();
}
public boolean visitEdge(Edge e)
// pre: sets visited flag on edge; returns previous value
{
return e.visit();
}
public boolean isVisited(Object label)
// post: returns visited flag on labelled vertex
{
GraphMatrixVertex vert;
vert = (GraphMatrixVertex) dict.get(label);
return vert.isVisited();
}
public boolean isVisitedEdge(Edge e)
// post: returns visited flag on edge
{
return e.isVisited();
}
public void reset()
// post: resets visited flags to false
{
Iterator it = dict.elements();
for (it.reset(); it.hasMoreElements(); it.nextElement())
((GraphMatrixVertex)it.value()).reset();
for (int row=0; row<size; row++)
for (int col=0; col<size; col++) {
Edge e = data[row][col];
if (e != null) e.reset();
}
}
public int size()
// post: returns the actual number of vertices in graph
{
return dict.size();
}
public int degree(Object label)
// pre: label labels an existing vertex
// post: returns number of vertices adjacent to label
{
// get index
int row = ((GraphMatrixVertex)dict.get(label)).index();
int col;
int result = 0;
// count non-null columns in row
for (col = 0; col < size; col++)
if (data[row][col] != null) result++;
return result;
}
abstract public int edgeCount();
// post: returns the number of edges in graph
public Iterator elements()
// post: returns iterator across all vertices of graph
{
return dict.keys();
}
public Iterator neighbors(Object label)
// pre: label is label of vertex in graph
// post: returns iterator vertices adj. to labeled vertex
{
GraphMatrixVertex vert;
vert = (GraphMatrixVertex) dict.get(label);
List list = new SinglyLinkedList();
for (int row=size-1; row>=0; row--)
{
Edge e = data[vert.index()][row];
if (e != null) {
if (e.here().equals(vert.label()))
list.add(e.there());
else
list.add(e.here());
}
}
return list.elements();
}
abstract public Iterator edges();
// post: returns iterator across all edges of graph
(returns Edges)
public void clear()
// post: removes vertices and edges from graph
{
dict.clear();
for (int row=0; row<size; row++)
for (int col=0; col<size; col++)
data[row][col] = null;
freeList = new SinglyLinkedList();
for (int row=size-1; row>=0; row--)
freeList.add(new Integer(row));
}
public boolean isEmpty()
// post: returns true iff graph is empty
{
return dict.isEmpty();
}
public boolean isDirected()
// post: returns true iff graph is directed
{
return directed;
}
}
Specialize for either directed or undirected graphs. E.g.,
public class GraphMatrixUndirected extends GraphMatrix
{
public GraphMatrixUndirected(int size)
// pre: size > 0
// post: constructs an empty graph that may be expanded
// to at most size vertices. Graph is directed if
// dir true and undirected otherwise
{
super(size,false);
}
public void addEdge(Object vLabel1, Object vLabel2, Object label)
// pre: vLabel1 & vLabel2 are labels of existing
// vertices, v1 & v2
// post: edge (possibly directed) is inserted btn v1 & v2
// if edge is new, it is labeled w/ label (can be null)
{
GraphMatrixVertex vtx1,vtx2;
// get vertices
vtx1 = (GraphMatrixVertex) dict.get(vLabel1);
vtx2 = (GraphMatrixVertex) dict.get(vLabel2);
// update matrix with new edge
Edge e = new Edge(vtx1.label(), vtx2.label(), label, directed);
data[vtx1.index()][vtx2.index()] = e;
data[vtx2.index()][vtx1.index()] = e;
}
...
}
Directed graph is similar.